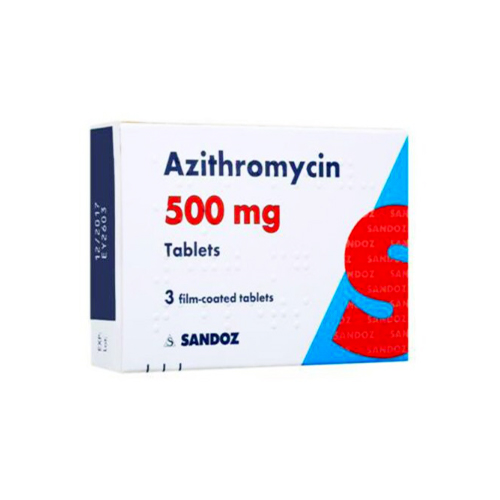
Azithromycin
Images for illustrative purposes only
- Clears Chlamydia
- Stops the growth of bacteria
- Effective antibiotic
Azithromycin
Azithromycin tablets belong to a group of medicines called macrolide antibiotics. It is used to treat infections caused by certain bacteria including Chlamydia.
Starting from
£16.99
Order within
to receive your order by
After selecting this product, you will need to complete a short assessment, so we can make sure this medication is suitable for you.
Quick & Easy
No appointment or long waiting times
Discreet Packaging
Plain packaging with no medical stamps or marks
Confidential Service
Your information always remains private
Registered Pharmacy
Dispensed by our UK registered pharmacy
About Azithromycin
What is Azithromycin?
Azithromycin belongs to a group of antibiotics called “Macrolides”
It is commonly used to treat a wide range of bacterial infections in the body which include:
· Chest, Throat and Nasal infections (bronchitis, tonsillitis, pneumonia, pharyngitis and sinusitis)
· Skin and soft tissue infections
· Ear infections
· Sexually transmitted infections (STI’s) caused by an organism called Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoea.
(AccessDoctor will prescribe Azithromycin for the purpose of treating sexually transmitted infections only).
How does Azithromycin work in treating sexually transmitted infections?”
The active ingredient in azithromycin targets and stops the production of enzymes in chlamydia (C.tacromatis) and gonorrhoea (N.gonorrhoea), responsible for growth and spread. This then helps the body to clear the infection.
How to use Azithromycin
For the purpose of treating Chlamydia, the recommended dose of Azithromycin is a single dose of 1g (2 x 500mg tablets) taken together in a single day either an hour before, or 3-hours after a meal. You should then take one capsule a day for the next 2 days (three days worth of treatment altogether).
The dosage is slightly different for treating Gonorrhoea, the recommended dose is 1g or 2g of Azithromycin in a single dose in combination with 250 or 500 mg of ceftriaxone, an hour before or 3-hours after a meal.
How can I get Azithromycin prescribed?
If you have already been diagnosed with chlamydia or Gonorrhoea at a sexual health clinic, GP or nurse, start by completing our online consultation form for one of our access doctors to review.
Once your treatment has been approved, our own pharmacy team will prepare and send out your treatment in unmarked and discreet packaging to the address of your choice.
Side effects & precautions
Tell one of our Access Doctors if you have or have had any of the following conditions:
- Liver problems: your doctor may need to monitor your liver function or stop the treatment
- Kidney problems
- Heart conditions
Azithromycin may interact with certain medications, so please tell us if you are taking any of the following:
- Colchicine (used for gout)
- Antacids (for indigestion)
- Warfarin or any similar medicines to prevent blood clots
- Ciclosporin (used to suppress the immune system to prevent and treat rejection of a transplanted organ or bone marrow)
- Digoxin (used to treat heart failure)
- Fexofenadine (for hay fever or a skin allergy)
Also, tell us if you are pregnant, or breastfeeding as this will help us decide if the treatment is right for you or not.
What are the side effects of taking Azithromycin?
As with all medications, Azithromycin may cause side effects in some people.
The most commonly seen side effects are as follows:
- Diarrhoea
- Vomiting
- Stomach cramps
- Nausea
- Indigestion/Trapped wind
- Skin rashes
- Dizziness
- Headaches
- Numbness of hands and feet (pins & needles)
- Loss of appetite
- Joint pains
However, as the treatment period for chlamydia and gonorrhoea infections is short, side effects are not usually noticed.


We’re here to help.
Our friendly team is available to help Monday to Friday 9:00am - 5:00pm.
If you need urgent assistance, do not use this service. Call 111, or in an emergency call 999.